Recovery Techniques
(Extraction of petroleum)
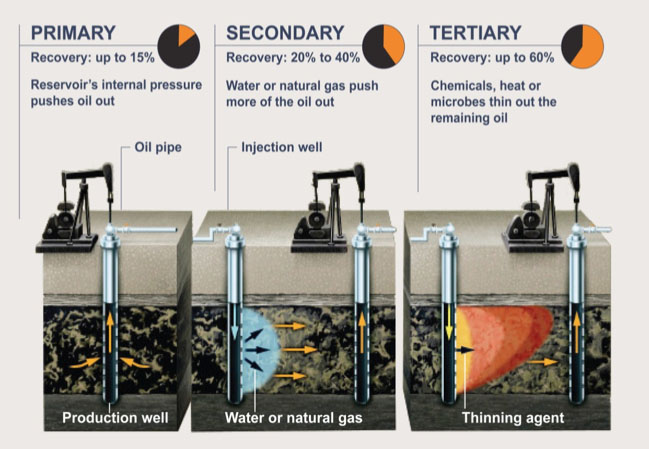
1.) Primary recovery
The majority of energy comes from reservoir, the natural mechanisms. These include expansion of the natural gas at the top of the reservoir, expansion of gas initially dissolved in the crude oil, natural water displacing oil downward into the well, and gravity drainage resulting from the movement of oil within the reservoir from the upper to the lower parts where the wells are located.
The majority of energy comes from reservoir, the natural mechanisms. These include expansion of the natural gas at the top of the reservoir, expansion of gas initially dissolved in the crude oil, natural water displacing oil downward into the well, and gravity drainage resulting from the movement of oil within the reservoir from the upper to the lower parts where the wells are located.
2.) Secondary recovery
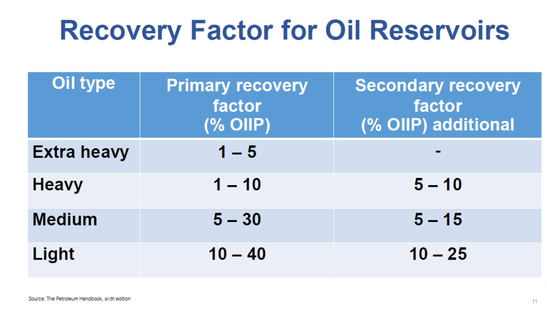
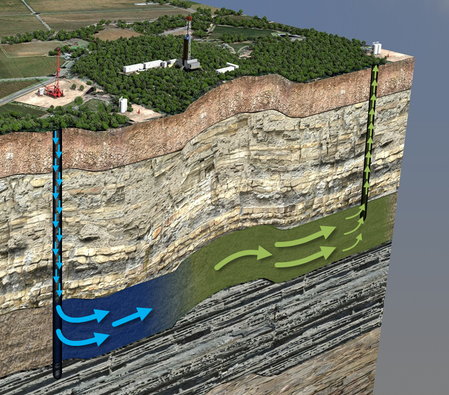
After the pressure falls and at some point, underground pressure is insufficient to force the oil to the surface. After natural reservoir energy decrease, secondary recovery methods are applied. They rely on the supply of external energy into the reservoir. Hence, secondary recovery techniques increase the reservoir’s pressure by water injection, natural gas reinjection and gas lift, which injects air, carbon dioxide or some other gas into the bottom of the well, reducing the overall density of fluid in the wellbore. on average, the recovery factor after primary and secondary oil recovery operations is between 35 and 45%, depending on the properties of the oil and the characteristics of the reservoir rock.
After the pressure falls and at some point, underground pressure is insufficient to force the oil to the surface. After natural reservoir energy decrease, secondary recovery methods are applied. They rely on the supply of external energy into the reservoir. Hence, secondary recovery techniques increase the reservoir’s pressure by water injection, natural gas reinjection and gas lift, which injects air, carbon dioxide or some other gas into the bottom of the well, reducing the overall density of fluid in the wellbore. on average, the recovery factor after primary and secondary oil recovery operations is between 35 and 45%, depending on the properties of the oil and the characteristics of the reservoir rock.
3.) Enhanced oil recovery (EOR) or Tertiary recovery
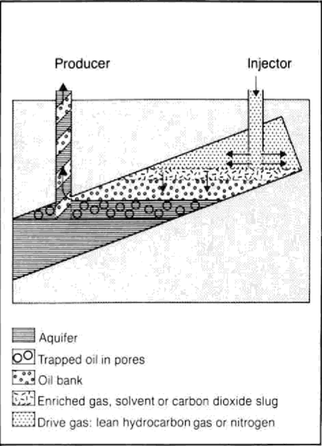
Increasing the mobility of the oil in order to increase extraction. According to the US department of Energy, there are three techniques for EOR which is thermal processes, gas injection(miscible processes) and chemical processes.
Increasing the mobility of the oil in order to increase extraction. According to the US department of Energy, there are three techniques for EOR which is thermal processes, gas injection(miscible processes) and chemical processes.
|
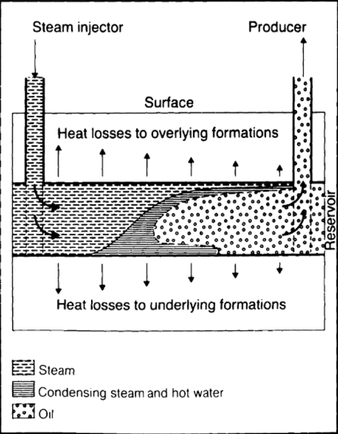
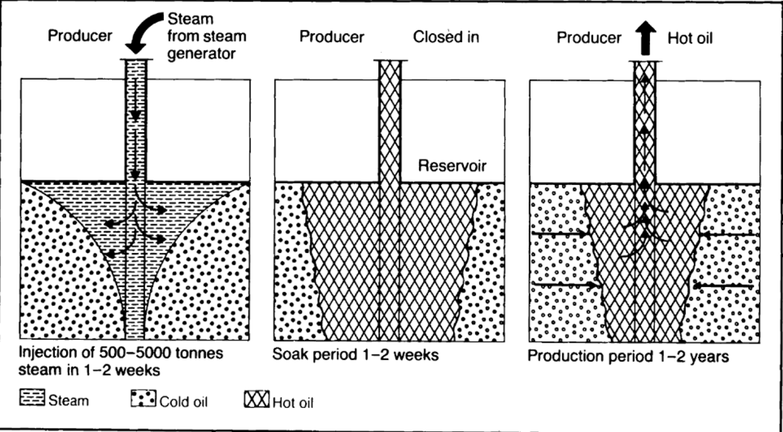
3.1) Thermal processes : using heat to reduce oil viscosity (for heavy oil)
3.1.1 Surface heat generation
|
|
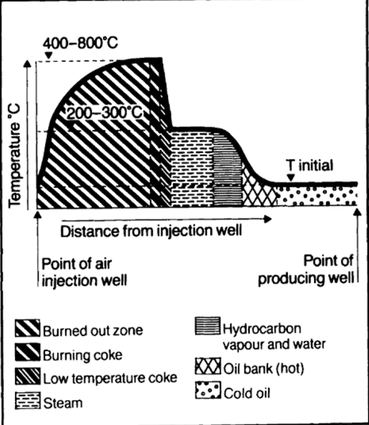
3.1.2 Underground heat generation
|
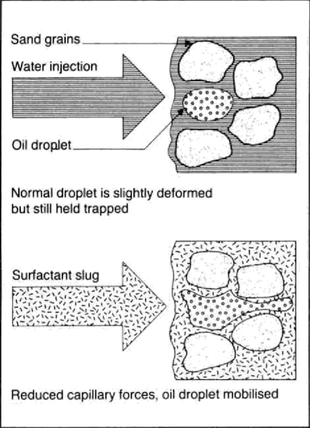
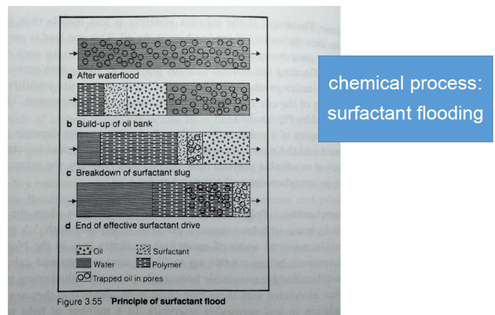
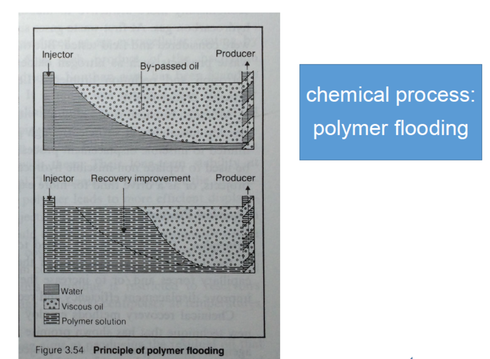
3.3) Chemical processes : to increase viscosity of displacing fluid (polymer flooding) and reduce capillary force (surfactant and caustic flooding)
|
Reference
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Extraction_of_petroleum#Enhanced_recovery
- https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Enhanced_oil_recovery#Thermal_injection
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/h/hot_waterflooding.aspx
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/s/steamflood.aspx
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/c/cyclic_steam_injection.aspx
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/f/fire_flooding.aspx
- http://csegrecorder.com/articles/view/enhanced-oil-recovery-techniques-and-nitrogen-injection
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/s/surfactant_flooding.aspx
- http://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/Terms/a/alkaline_flooding.aspx
- http://halliburtonblog.com/considerations-for-waterflooding-in-mature-fields-reservoir-optimization/
- http://susris.com/wp-content/uploads//2014/01/figure1.jpg
- The Petroleum Handbook, sixth edition