The Exploration techniques for Petroleum can be separated into two ways; surface geology and subsurface geology.
Surface geology
-Direct Indications:
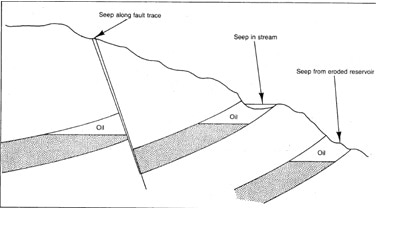
When we explore for oil and gas, we will observe on many indications especially on oil and gas that upon the ground through the seep along fault trace, porous rock, oxidation of petroleum reduces that volatile constituents and some plant forms.
Surface geology
-Direct Indications:
When we explore for oil and gas, we will observe on many indications especially on oil and gas that upon the ground through the seep along fault trace, porous rock, oxidation of petroleum reduces that volatile constituents and some plant forms.
Oil and gas upon the ground.
-Surface Data
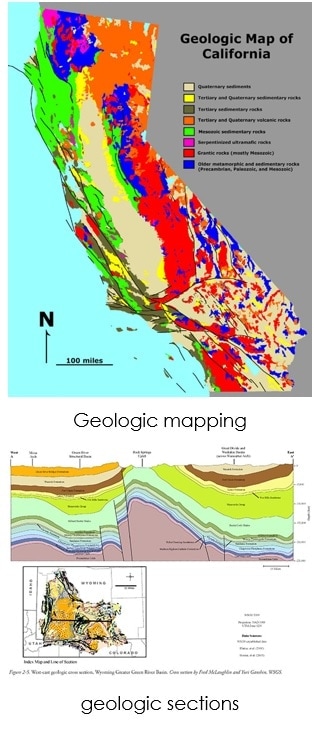
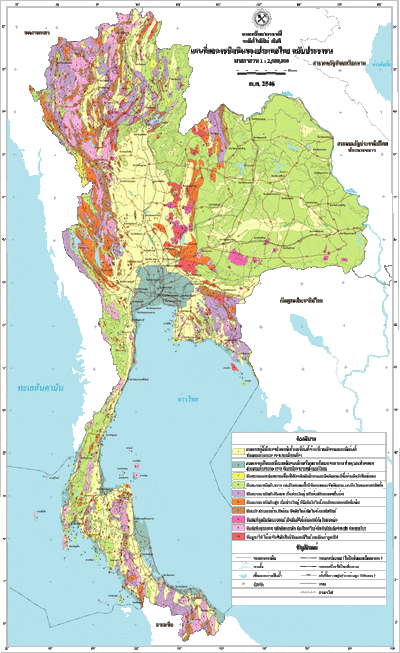
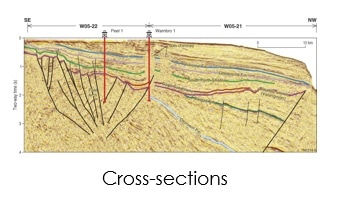
Essential when rock appear at the surface. We will accumulate the data from engineering measuring instrument. We will search on many important things such as Geologic mapping that plot geologic data on the map, their thicknesses and distribution that are essential in an exploration area where the place without source and reservoir rock, correlation of geologic sections that make us know the information of the rock sections, photogeology or aerial photographs and we will also search on cross-sections including stratigraphy, structure, porosity, lithology, and thickness of important formations all of these will help you in exploration
Field Geology
-traditional method of finding oil
-mapping the surface geology and studying the relationship to geological units
-to predict and understand the types of rock in the subsurface
-Surface Data
Essential when rock appear at the surface. We will accumulate the data from engineering measuring instrument. We will search on many important things such as Geologic mapping that plot geologic data on the map, their thicknesses and distribution that are essential in an exploration area where the place without source and reservoir rock, correlation of geologic sections that make us know the information of the rock sections, photogeology or aerial photographs and we will also search on cross-sections including stratigraphy, structure, porosity, lithology, and thickness of important formations all of these will help you in exploration
Field Geology
-traditional method of finding oil
-mapping the surface geology and studying the relationship to geological units
-to predict and understand the types of rock in the subsurface
Airborne Imagery
-photograph the whole area from the air
-use aircraft with high-resolution wide-angle camera flies over the area and takes photographs
- Now: a new series of satellite images have improved with resolution of about 15 meters and can produce stereoscopic images worldwide
-photograph the whole area from the air
-use aircraft with high-resolution wide-angle camera flies over the area and takes photographs
- Now: a new series of satellite images have improved with resolution of about 15 meters and can produce stereoscopic images worldwide
Moreover, we can adapt the new technology to help for exploring the petroleum. This technique is called Geophysics which is field survey conduct consist of magnetic field, gravity field, seismic reflection. All of these methods can analyzed the physical information.
Gravimetric method
-measurements of very slight variations in the force of gravity at the surface of the earth
-using gravimeters
-force of gravity at any point on the earth’s surface is influences in magnitude and direction by the distribution of rocks of different densities under the area
-Older rocks tend to have stronger gravitational force than the sediments of the newer basins
-measurements of very slight variations in the force of gravity at the surface of the earth
-using gravimeters
-force of gravity at any point on the earth’s surface is influences in magnitude and direction by the distribution of rocks of different densities under the area
-Older rocks tend to have stronger gravitational force than the sediments of the newer basins
Magnetic method
-measuring variations in the intensity of the earth’s magnetic field
-using sensitive instruments known as magnetometers, which can be used on land, at sea, or in aircraft
-localised magnetic variations come from the varying magnetic properties of the underlying rocks
-ocean-floor lavas have a stronger magnetic force than marine limestones
-Magnetic surveys are useful for gathering regional framework of sedimentary basins before expensive seismic surveys are used
-measuring variations in the intensity of the earth’s magnetic field
-using sensitive instruments known as magnetometers, which can be used on land, at sea, or in aircraft
-localised magnetic variations come from the varying magnetic properties of the underlying rocks
-ocean-floor lavas have a stronger magnetic force than marine limestones
-Magnetic surveys are useful for gathering regional framework of sedimentary basins before expensive seismic surveys are used
Seismic method
-measurement at the surface of waves which have been generated by a source and have travelled through the earth
-can be used both onshore and offshore
-there are 3 components in the data acquisition system: the source, the detector, and the recording equipment
-measurement at the surface of waves which have been generated by a source and have travelled through the earth
-can be used both onshore and offshore
-there are 3 components in the data acquisition system: the source, the detector, and the recording equipment
|
|
|
Electrical method
-depends on differences in the resistance to electric currents by rocks of various types
-rarely used as surface exploration techniques
-In the subsurface, this method is used in various well-logging tools which help to identify formations that are drilled through
-depends on differences in the resistance to electric currents by rocks of various types
-rarely used as surface exploration techniques
-In the subsurface, this method is used in various well-logging tools which help to identify formations that are drilled through
Subsurface Geology
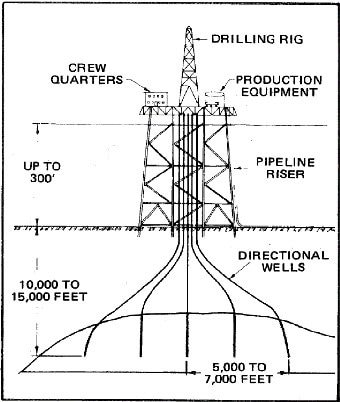
When we explore in subsurface geology, we could not know the subsurface appearances until we drill the well. Then, we will show the drilling operation first that how we use the equipment and its abilities.
We need to drill the first well for exploration because we couldn’t know that the area has petroleum or not unless we drill it. The first drilling well for exploration we call it “wildcat well”.
This picture shows about the drilling operational unit. I will show you about some important equipment including diesel engines, cable, derrick, drill mud which is pumped from the mud tank through the standpipe, rotary hose, swivel into the Kelly for decreasing the temperature of the drill pipe and bring the rock waste to the surface, a blowout preventer which installs below the derrick floor to control pressure zone and prevent equipment damage, the drill equipment such as drill pipe, drill collars, and a drill bit.
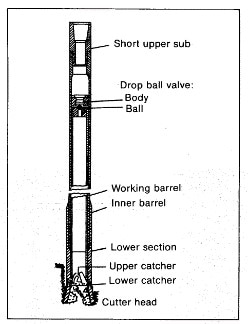
Therefore, when we have finished to drill the well, we will analyze the information of the formation in many ways. We will start analyzed the example of the rock that is called a core sample.
A core sample is a cylinder section of sample rock that we collect from the drilling well for investigating the rock properties such as permeability, water saturation. It is inspected and analyzed by different techniques and equipment depending on the type of data desired.
After we obtain primary information from a core sample, we will analyze more information by wireline well-logging techniques that measurements are made of the electrical, radioactive and acoustic properties of rock. All of these measurements can tell a lot of important information including density, radioactivity, porosity, conductivity, resistivity, fluid saturation and permeability, formation depth, thickness, fluid type.
A core sample is a cylinder section of sample rock that we collect from the drilling well for investigating the rock properties such as permeability, water saturation. It is inspected and analyzed by different techniques and equipment depending on the type of data desired.
After we obtain primary information from a core sample, we will analyze more information by wireline well-logging techniques that measurements are made of the electrical, radioactive and acoustic properties of rock. All of these measurements can tell a lot of important information including density, radioactivity, porosity, conductivity, resistivity, fluid saturation and permeability, formation depth, thickness, fluid type.
Reference:
http://www.eegs.org/what-is-geophysics-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Core_sample
https://geonoi.files.wordpress.com/2015/10/geologic-map-of-thailand1.gif?w=627&h=1024
https://pangea.stanford.edu/research/groups/structure/gfx/lidarSAF.jpg
http://www.geologyforinvestors.com/wp-content/uploads/GravitySurveys.jpg
https://crustal.usgs.gov/projects/rgb/images/drenth/image022.jpg
https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1999/of99-514/gif/method.gif
https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=5768333d3d7f4b31ce156a94&assetKey=AS%3A375119345143808%401466446829376
Basic Petroleum geology book by Peter K Link P.341-382
Written by MR. Xuxun Huang
MS.Samita Dhangwattanotai
http://www.eegs.org/what-is-geophysics-
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Core_sample
https://geonoi.files.wordpress.com/2015/10/geologic-map-of-thailand1.gif?w=627&h=1024
https://pangea.stanford.edu/research/groups/structure/gfx/lidarSAF.jpg
http://www.geologyforinvestors.com/wp-content/uploads/GravitySurveys.jpg
https://crustal.usgs.gov/projects/rgb/images/drenth/image022.jpg
https://pubs.usgs.gov/of/1999/of99-514/gif/method.gif
https://www.researchgate.net/file.PostFileLoader.html?id=5768333d3d7f4b31ce156a94&assetKey=AS%3A375119345143808%401466446829376
Basic Petroleum geology book by Peter K Link P.341-382
Written by MR. Xuxun Huang
MS.Samita Dhangwattanotai