INORGANIC OR ABIOTIC ORIGIN
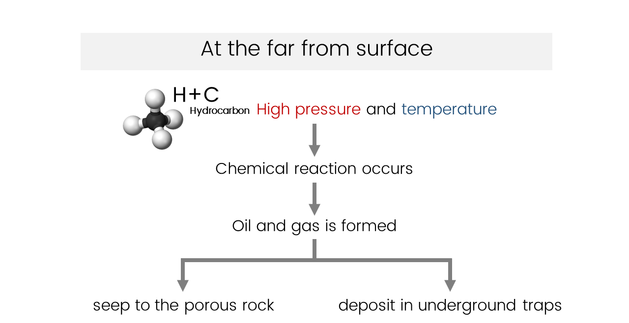
Inorganic origin theories state that petroleum is formed from Earth itself, due to
chemical interactions deep within the Earth.
chemical interactions deep within the Earth.
These theories assume that petroleum is not finite
as substances like oil and gas didn’t run out of till now.
as substances like oil and gas didn’t run out of till now.
Let's take it easy with a flow chart
This theory has 4 sub-theories
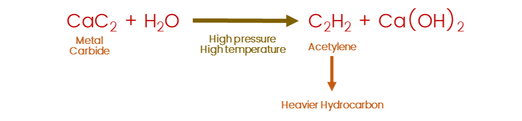
Metal carbide theory
This theory is stated by a Russian Chemist.
He told that "Deposition of petroleum is controlled by tectonic activities (Occur during life of sedimentary rock)"
This theory is explained by the "Metal carbide theory"
He told that "Deposition of petroleum is controlled by tectonic activities (Occur during life of sedimentary rock)"
This theory is explained by the "Metal carbide theory"
Volcanic theory
The gas will be released from traps of the mantle via volcanic activity or eruption.
Earthquake
The gas will be released from deep parts in Earth's mantle via tectonic activities, such as faults.
Serpentinization
Hydrocarbons are a by-product from metamorphic transformation of green, dark Olivine minerals (in Earth's mantle).
ORGANIC ORIGIN
|
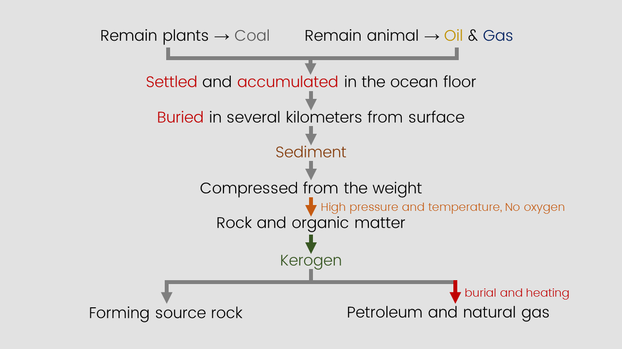
Organic origin theory states that petroleum are finite substances which are formed from organisms decaying in the subsurface |
Reference: www.7diphone.com
|
Let's take it easy with a flow chart
ADDITIONAL KNOWLEDGE
- Most hydrocarbons are produced close to belts of tectonic activities
- Brine is present in petroleum
- Petroleum is found only in sedimentary rocks not in igneous or metamorphic rocks
- The organic carbon found in plants is depleted into C13 from photosynthesis process
- Dead organic matter is depleted by radioactive decaying
- Both of depletion above is found in petroleum & natural gas
- Brine is present in petroleum
- Petroleum is found only in sedimentary rocks not in igneous or metamorphic rocks
- The organic carbon found in plants is depleted into C13 from photosynthesis process
- Dead organic matter is depleted by radioactive decaying
- Both of depletion above is found in petroleum & natural gas
Reference
http://petrowiki.org/Origin_of_petroleum
http://petrowiki.org/Origin_of_petroleum