Petrophysics
by Xuxun Huang
by Xuxun Huang
Petrophysics is the subject that we study in rock properties and their interactions with fluids such as gases, liquid hydrocarbon, water. We study many things including porosity, permeability, physical properties that related to their storage and transmission of fluids.
First of all, the properties of rock depend on mineral composition, grain size, orientation, amount of cementation, and compaction. All these have affected on rock properties
Mineral composition. most of the rock in earth crust have minerals that include only 8 main elements including O, Si, Al, Fe, Ca, Na, Mg, K. Moreover, we can be accomplished these elements by emission spectrography and X-ray dispersive scanning electron microscopy. Then, each of mineral have their specific properties depending on their minerals.
Grain size and orientation will have affected on rock properties such as when the rock had small grain size and good orientation, the rock would have low porosity. Then, this porosity will relate to permeability but it didn’t mean that high porosity will have high permeability. However, it was depended on the kind of rock. Moreover, cementation will relate to the porosity. The deeper height will have more cementation and less porosity.
Basic knowledge about Petrophysics.
|
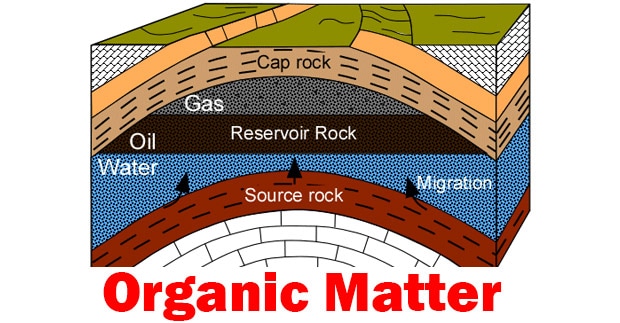
Next, we will consider the type of rocks. If we consider in their duties, we will consider in three types for this subject. First is source rock, cap rock, reservoir rock. The cap rock has already explained in accumulation and traps topic, source rock also has already published in evaluation of source rocks topic. The last reservoir rock has also already published in the reservoir topic. You can read more at Moreover, we can also consider the type of rocks by geology that can be separated into 3 types of rocks including igneous rocks that are produced by cooling of magma, Metamorphic rocks that are originated from mechanical, thermal, and chemical changes of other igneous rocks. The last, sedimentary rocks are produced by sedimentation. |
Reference :
Dr. Raphael Bissen in General Geology subject.
Dr.Falan Srisuriyachai in rock and Fluid Properties subject.
Dr. Raphael Bissen in General Geology subject.
Dr.Falan Srisuriyachai in rock and Fluid Properties subject.