WHAT IS TRAP!!!!!
Accumulation and Traps
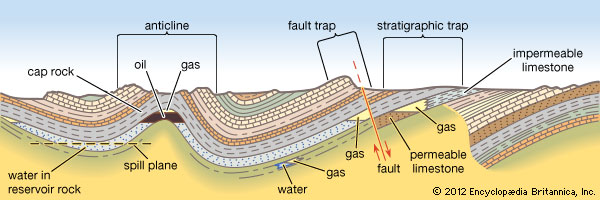
A trap is the place where oil and gas are barred from further movement
----Levorsen 1967-----
----Levorsen 1967-----
underground rock formation that blocks the movement of petroleum and causes it to accumulate in a reservoir that can be exploited
The oil is accompanied always by water and often by Natural gas
-confined in a porous and permeable reservoir rock (Sedimentary rock )
The natural gas occupies the top of the trap and is underlain by the oil and then the water.
A layer of impermeable rock, called the cap rock, prevents the upward or lateral escape of the petroleum.
That part of the trap actually occupied by the oil and gas is called the petroleum reservoir.
The oil is accompanied always by water and often by Natural gas
-confined in a porous and permeable reservoir rock (Sedimentary rock )
The natural gas occupies the top of the trap and is underlain by the oil and then the water.
A layer of impermeable rock, called the cap rock, prevents the upward or lateral escape of the petroleum.
That part of the trap actually occupied by the oil and gas is called the petroleum reservoir.
Trap And Accumulation
Underground rock formation that blocks the movement of petroleum and cause accumulation
|
Happen when changing in
subsurface structural |
deposition or diagenetic
features in the sedimentary |
Combination Trap
|
Many systems have been proposed for the classification of traps
one simple system divides them into
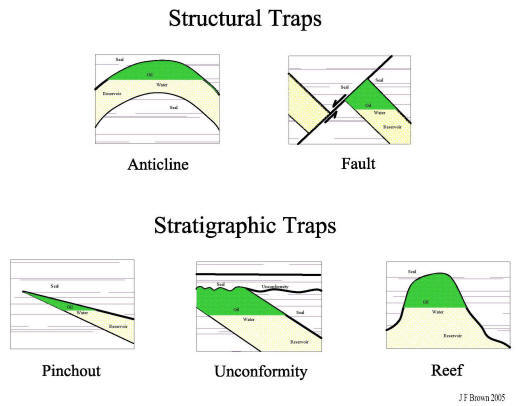
1.Structural Trap
the most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock.
In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir.
Another kind of structural trap is the Fault Trap. The fracture and slippage of rock along a Fault line may bring an impermeable stratum in contact with a layer of permeable reservoir rock and thus forms a barrier to petroleum migration
2.Stratigraphic traps
variations within the rock strata themselves (e.g., a change in the local porosity and permeability of the reservoir rock, a change in the kinds of rocks laid down, or a termination of the reservoir rock) play the important role.
The stratigraphic variations associated with the reservoir rocks are the main influence on the areal extent of the reservoirs in these traps.
The oil and gas pool will rise to the top of the trap if the underlying water is stationary, and the resulting oil-water contact will be level. When the water is moving, however, the pool is displaced down the trap’s side in the direction of flow because of hydrodynamic pressure.
In some traps, the pool may be displaced great distances or may even be completely flushed out. In addition Salt dome is included.
3. Hydrodynamic traps- are a far less common type of trap. They are caused by the differences in water pressure, that are associated with water flow, creating a tilt of the hydrocarbon-water contact.
one simple system divides them into
1.Structural Trap
the most common type of structural trap is formed by an anticline, a structure with a concave roof caused by the local deformation of the reservoir rock and the impermeable cap rock.
In this case, the intersection of the oil-water contact with the cap rock determines the edges of the reservoir.
Another kind of structural trap is the Fault Trap. The fracture and slippage of rock along a Fault line may bring an impermeable stratum in contact with a layer of permeable reservoir rock and thus forms a barrier to petroleum migration
2.Stratigraphic traps
variations within the rock strata themselves (e.g., a change in the local porosity and permeability of the reservoir rock, a change in the kinds of rocks laid down, or a termination of the reservoir rock) play the important role.
The stratigraphic variations associated with the reservoir rocks are the main influence on the areal extent of the reservoirs in these traps.
The oil and gas pool will rise to the top of the trap if the underlying water is stationary, and the resulting oil-water contact will be level. When the water is moving, however, the pool is displaced down the trap’s side in the direction of flow because of hydrodynamic pressure.
In some traps, the pool may be displaced great distances or may even be completely flushed out. In addition Salt dome is included.
3. Hydrodynamic traps- are a far less common type of trap. They are caused by the differences in water pressure, that are associated with water flow, creating a tilt of the hydrocarbon-water contact.
Seal and Caprock
A seal is an impervious or impermeable bed capping
the reservior rock in a trap
the reservior rock in a trap
Vertical and Lateral sealA typical type of seal
|
Force related to sealCapillary may be used to quantify the
quality or effectiveness |
Seal
- Rocks that forms a barrier or cap above and around reservoir rock forming a trap such that fluids cannot migrate beyond the reservoir. The permeability of a seal capable of retaining fluids through geologic time is ~ 10-6 to 10-8 darcies. commonly
- A seal is a critical component of a complete petroleum system.
Capillary Force
is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Occurs because of intermolecular force between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension
- Rocks that forms a barrier or cap above and around reservoir rock forming a trap such that fluids cannot migrate beyond the reservoir. The permeability of a seal capable of retaining fluids through geologic time is ~ 10-6 to 10-8 darcies. commonly
- A seal is a critical component of a complete petroleum system.
Capillary Force
is the ability of a liquid to flow in narrow spaces without the assistance of, or even in opposition to, external forces like gravity. Occurs because of intermolecular force between the liquid and surrounding solid surfaces. If the diameter of the tube is sufficiently small, then the combination of surface tension
AUTHOR/EDITOR

Hello...
My name is Pattanan Thamrujikul
I'm Studying in the faculty of Engineering Chulalongkorn university
As a major of petroleum engineering.
HOPE YOU ENJOY:)))