Basin EnvironmentAuthor Phoomphavis Boonsrirojna Editor Poomisant Srimaharaja
What is a basin?
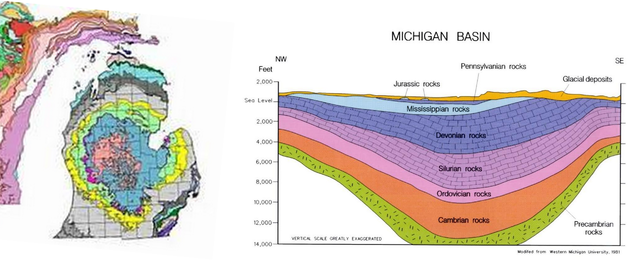
From the dictionary, basin is an open shallow usually a round container used especially for holding liquids. (from www.thefreedictionary.com) Here we will talk about basin that is a sedimentary basin not the basin that is used in the toilet, so it is a geological basin. But from this definition it is still hard to understand, so the best way is to show you some pictures of the basins. So, in this picture you can see that this basin is pulled downward and it has a characteristic that can keep liquid in the bottom of it.
Why this is important?
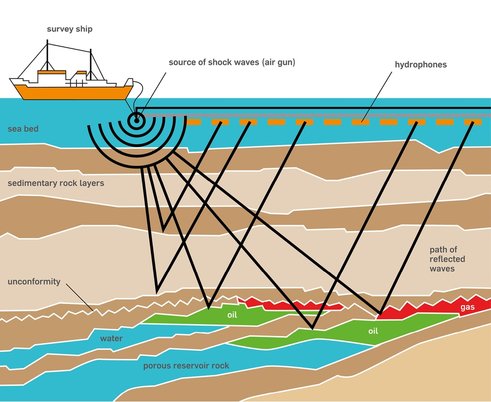
When we start the exploration for petroleum, one of the first places that has a chance to contain oil and gas usually is place that has basin characteristic. This why the type of basins is the thing that is important to know. Type of basins
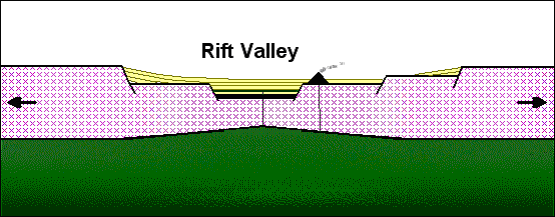
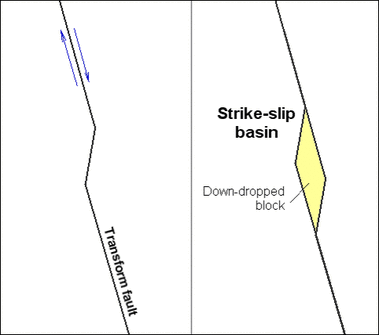
1. Rift-related basins
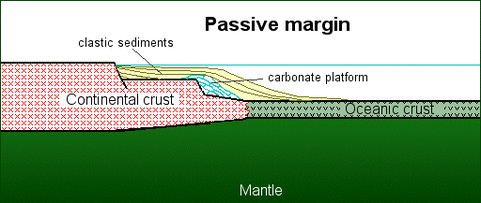
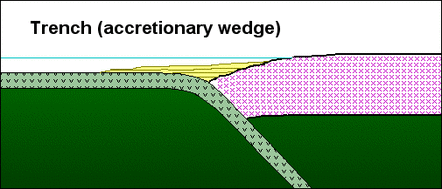
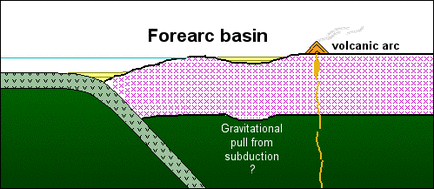
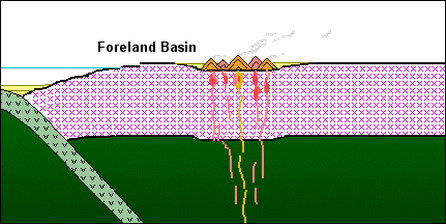
2. Subduction-related basins
|
PETROLEUM GEOLOGY
- Home
- Introduction
-
Content
- Petroleum Geochemistry
- Origin of Petroleum >
- Accumulation and Traps >
- The Reservoir >
- Shale oil >
-
More about Petroleum
>
- Types of drilling bits
- Crude oil emulsion
- Drilling Fluids/Mud and Components
- Oil-Rich Countries
- Facts about Petroleum
- Oil Measurement Unit
- Forecast of Energy Usage
- Exploration Techniques
- Geologist & Engineer
- Impacts on environment
- World Reserves
- Petroleum in Thailand
- NOC & IOC
- Digital Oilfields
- Career in PE
- Blowout Preventer(BOP)
- HSE Basic Concepts
- Geophysics >
- From Exploration to Refining
- Well logging
- Real-Time Oil Price
- Glossary of Oil and Gas Terms
- Petroleum management systems
- Contact
- About