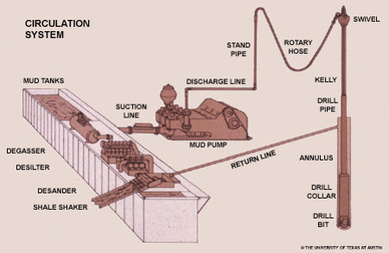
Drilling Fluids/Mud and Components
written and prepared by Tapapas Rattanachaikanon (PE36) - Oatshadow
What are Drilling Fluids?
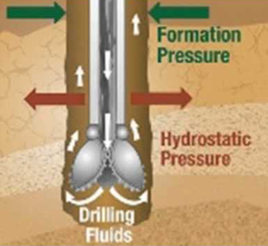
Drilling Fluids, also called drilling mud, in petroleum engineering, a heavy, viscous fluid mixture that is used in oil and gas drilling operations to carry rock cuttings to the surface and also to lubricate and cool the drill bit. The drilling mud, by hydrostatic pressure, also helps prevent the collapse of unstable strata into the borehole and the intrusion of water from water-bearing strata that may be encountered.
The drilling fluid system is commonly known as the “mud system”. It is the single component of the well-construction process that remains in contact with the wellbore throughout the entire drilling operation. Drilling fluid systems are designed and formulated to perform efficiently under expected wellbore conditions. Advances in drilling fluid technology have made it possible to implement a cost-effective, fit-for-purpose system for each interval in the well-construction process.
Overview of Drilling Fluids/Mud
The active drilling fluid system comprises a volume of fluid that is pumped with specially designed mud pumps from the surface pits. It travels through the drill string exiting at the bit, up the annular space in the wellbore, and back to the surface for solids removal and maintenance treatments as needed. The capacity of the surface system usually is determined by the rig size, and rig selection is determined by the well design.
For example, the active drilling-fluid volume on a deep water well might be several thousand barrels. Much of that volume is required to fill the long drilling riser that connects the rig floor to the seafloor. By contrast, a shallow well on land might only require a few hundred barrels of fluid to reach its objective.
Types of Drilling Fluids
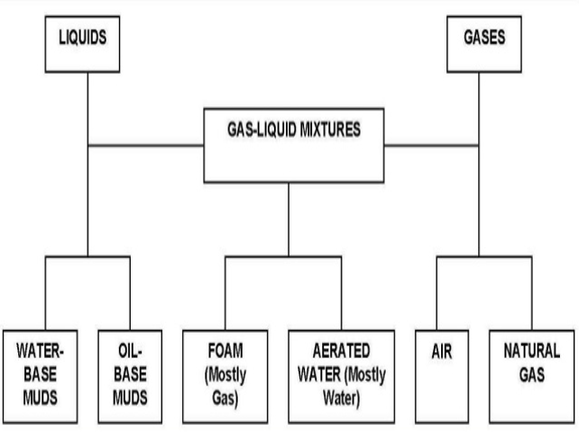
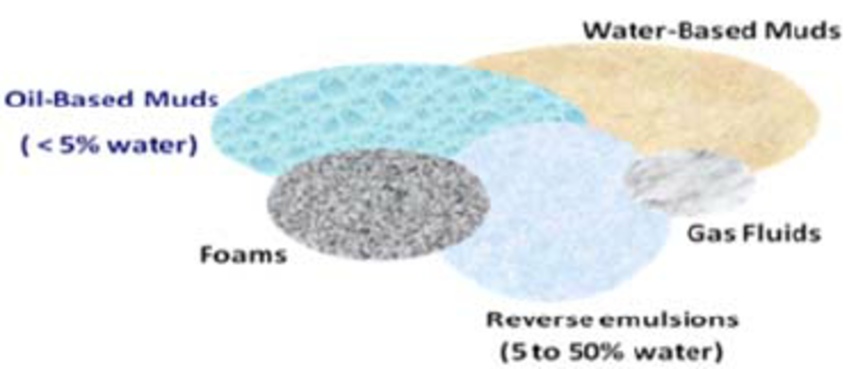
There are many types of drilling fluids are used on a day-to-day basis. Some wells require that different types be used at different parts in the hole, or that some types be used in combination with others. The various types of the fluid generally fall into a few broad categories.
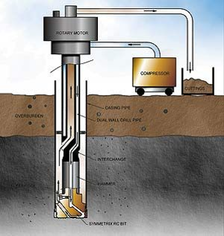
1. Air Drilling (Air Fluids)
|
Compressed air is pumped either down the bore hole's annular space or down the drill string itself.
The advantages of an air drilling are... • higher penetration rates • Better hole cleaning • Less formation damage The disadvantages of an air drilling are... • Cannot support the wellbore stability • Doesn’t provide enough pressure |
2. Water Based Mud
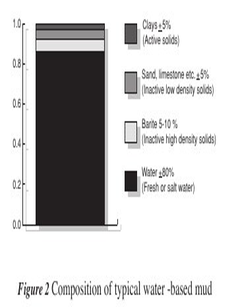
The most basic water-based mud systems begin with water, then clays and other chemicals are incorporated into the water to create a homogeneous blend resembling something between chocolate milk and a malt (depending on viscosity).
The fluid is the mud in which water is the continuous phase. This is the most common drilling mud used in oil drilling. The following designations are normally used to define the classifications of water base drilling fluid.
The fluid is the mud in which water is the continuous phase. This is the most common drilling mud used in oil drilling. The following designations are normally used to define the classifications of water base drilling fluid.
|
The advantages of the water based mud are...
• Considered less expensive than oil-based fluids (OBFs) or synthetic-based fluids (SBFs) • Commercial clays hydrate more • Most chemicals are more soluble The disadvantages of the water based mud are... • Formation clays would hydrate more • Make problem in borehole instability |
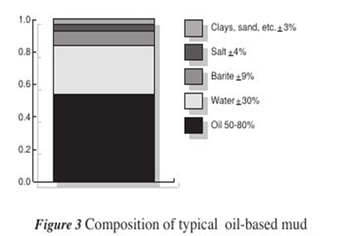
3. Oil Based Mud
Oil-based mud is a mud where the base fluid is a petroleum product such as diesel fuel. Oil-based muds are useful for many reasons, such as increasing the lubricity, enhanced the shale inhibition, greater cleaning abilities with less viscosity, and the oil-based muds also withstand greater heat without breaking down.
There are 2 types of oil-based muds which are Invert emulsion oil muds and Pseudo oil based muds.
If the amounts of water are more than 5 %. It will become water-in-oil emulsion or Invert emulsion.
All solids in Oil-based mud are considered inactive, because they do not react with oil.
There are 2 types of oil-based muds which are Invert emulsion oil muds and Pseudo oil based muds.
If the amounts of water are more than 5 %. It will become water-in-oil emulsion or Invert emulsion.
All solids in Oil-based mud are considered inactive, because they do not react with oil.
|
The advantages of the oil based mud are...
• Good properties at high temperature • More inhibition than water-based mud • Effective against all types of corrosion • Good lubricating characteristics • Permits mud in the low densities The disadvantages of the oil based mud are... • Higher initial cost • Requires more pollution-control procedures • Reduced effectiveness of some logging tools • Treatment for lost circulation is more difficult • Detection of gas-kick is very difficult, because gas is soluble in oil • This mud has hazardous vapors which will cause health problems |
4. Synthetic Based Mud
Synthetic-based fluid is a mud where the base fluid is a synthetic oil. This is most often used on offshore rigs because it has the properties of an oil-based mud, but the toxicity of the fluid fumes are much less than an oil-based fluid. Synthetic-based fluid poses the same environmental and analysis problems as oil-based fluid.
How to selected the Drilling Fluids?
Drilling Fluid Functions
Factors that influencing the drilling fluid performance
The Components of Drilling Fluids/Mud
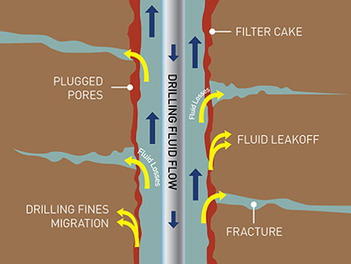
Water-based drilling mud most commonly consists of Bentonite clay (gel) with additives such as Barium sulfate (Barite), Calcium carbonate (chalk) or Hematite. Various thickeners are used to influence the viscosity of the fluid, e.g. xanthan gum, guar gum, glycol, or starch. Some other common additives including lubricants, shale inhibitors, and the fluid loss additives.
A weighting agent such as Barite is added to increase the overall density of the drilling fluids. Sufficient bottom hole pressure can be maintained thereby preventing an unwanted (and often dangerous) influx of formation fluids. Using of silica and clay nanoparticles for high pressure and high temperature help to get an Invert emulsion based muds and to observed their positive effect on the rheology of the drilling mud.
Useful Video clip about Drilling Fluids/Mud
Here's a Drilling Fluids/Mud video powered by Audiopedia, Youtube.
This video clip will use for academic purposes only, Thank you.
REFERENCES
https://petrowiki.org/Drilling_fluids
https://petrowiki.org/Drilling_fluid_types
https://petrowiki.org/Functions_of_drilling_fluid
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drilling_fluid
http://wiki.aapg.org/Drilling_fluid
https://www.britannica.com/technology/drilling-mud
https://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/en/Terms/d/drilling_fluid.aspx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTokgOnnU54
https://petrowiki.org/Drilling_fluid_types
https://petrowiki.org/Functions_of_drilling_fluid
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Drilling_fluid
http://wiki.aapg.org/Drilling_fluid
https://www.britannica.com/technology/drilling-mud
https://www.glossary.oilfield.slb.com/en/Terms/d/drilling_fluid.aspx
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=qTokgOnnU54